Writing in poetry has always been a great way people Express themselves. So it offers authors an unlike way to tell their feelings, their thought and their life. By its rich wording, rhythm, and profound message, poetry enables us to traverse the intricate details of the human experience in a condensed way. No matter you are an experienced poet or you would like to new creative activity, it’s a very rewarding experience writing poetry. This tutorial will take you through the basics of how to write a poem, a step-by-step guide, some tips and an introduction to tools, for example, Arvin AI, that can assist with your creative process.
What is Poetry?
Even as a concept, the idea of poetry in general is an expressive body of writing in which language is deployed to emphasize emotion, imagination and beauty. Though in prose, relatively simple convention of telling and simplicity in expressing thought may reign, in poetry experience is often condensed to sundering potent enough to be open to speculation. Poets, on the other hand, can convey deep insights, stir up particular emotions, and produce also striking imagery by artful choice of language, with respect to form and metrical structure. This means poetry is a strong medium for both writers and readers to have an introspective conversation with what is going on the world.
Types of Poems
Poetry comes in many forms, each with unique structures and characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
- Sonnets: A traditional form that commonly contains 14 lines, usually following a specific rhyming pattern, such as in the Shakespearean sonnet. Sonnets often examine love, nature, happy birthday poems and beauty.
- Haikus: A small, three-line poem that originally came from Japan; it traditionally deals with nature and the time of year. Haikus are 5-7-5 syllables in pattern.
- Free Verse: This is a less formal type of how to write a poem that doesn’t necessarily have a specific rhyme or meter. Free verse gives a poet more freedom to play with language and form.
- Limericks: Usually humorous in nature, these are five-line poems about life with a strong anapestic meter and the AABBA rhyming pattern.
The Role of Imagery, Rhythm, and Emotion in Poetry
- Imagery: Poetic imagery is the employment of words, which allow the mind to form certain vivid perceptions and to think in terms of the senses. It provides a strong mental picture that helps a reader be able to relate more fully to your how to write a poem. Whether describing a landscape or an emotion, imagery adds depth to your words.
- Rhythm: Rhythm is the pattern that has taken place in relation to sound and beat. For form in poetry, one sees it as fundamentally constituting the musical aspect within any poem. These often characterize moods to pieces to provide even more emotional shading on something there in the work.
- Emotion-Poetry is the medium that conveys joy, sadness, anger, love with wife or husband, or any feeling of man. With carefully chosen words, rhythm, and imagery, a poet might elicit from the reader what could be a very strong intimate moment in one’s life.
Finding Inspiration for How to Write a Poem
The most straightforward inspiration usually stems from life experiences. It could have been a reflection of one’s past relationship, a pivotal event in life, or even a moment of calm introspection, but where personal experiences will always excel is in the poet’s resonating with his audience. Writing from personal memory not only brings authenticity to the how to write a poem but also helps create a relatable narrative that others may find them in. Your emotions, reflections, and struggles are a goldmine for powerful poetic expression.
Exploring Nature and the World Around You
Another strong source of inspiration is nature. The world in front of us, a stroll in the woods, the roar of a thunderstorm, the beauty of a sunset—all matter for poetry. Nature’s constant changing and patterning provides fertile imagery and often stirs a range of emotions, from serenity to awe. The mystery of natural beauty and the power of nature can be used to help you in the art of writing poetry to audiences on a visceral and emotional level.
Using Prompts and Creative Challenges
Whether you’re exploring love, grief, hope, or despair, writing about your feelings allows you to express complex emotional truths that might be hard to convey through other forms of writing. If you find yourself stuck, using prompts and challenges can be incredibly helpful. These can be as simple as writing about the first thing you see when you wake up or even making a poem based on a certain word or theme. These are good to push the limits of your mind and can help to get rid of writer’s block.
Observing and Engaging with Your Environment
Finally, taking in the world around you is an excellent way to gain inspiration. Take the time to watch the world-people watch, listen to music, go to new places-and just let these moments marinate and get those creative juices flowing. If you remain open to the world happening around you, both in grand and small moments, inspiration for your how to write a poem will flow organically. And with a little practice, the possibilities of writing poetry will become endless.
The Structure of a Poem
Poem structure is one of the most influential aspects with regards to the impact of a poem. Poetic structures describe the structure of a how to write a poem in terms of its lines, stanzas, rhyme, and meter. Poets can have a large variety of forms, for example, sonnets, haikus and ballads. Such compositions typically come with a collection of pre-defined rules, for example a rhyme scheme, e.g. ABAB, or syllabic rhythm, which the poet has to follow strictly. Meter, the stress and unstressed pattern of the syllables in a line, is also very important in producing the structure of a poem.
Free Verse vs. Structured Poetry
Poetry can either follow a strict form or embrace freedom. Structured poetry, like sonnets or villanelles, adheres to specific rhyme schemes and meter patterns. These forms offer constraints that can inspire creativity and discipline, forcing the poet to think within boundaries. Structured poetry is often chosen for its traditional beauty and the challenge it presents in crafting meaning while adhering to strict rules. On the other hand, free verse does not follow any pattern or rhyme; thus, the poet enjoys complete freedom of expression.
Line Breaks and Stanzas
How a poem’s lines and stanzas are set up will have a radical effect on its flow and emphasis. Line breaks—the purposeful decision to terminate a line—serve to regulate the speed at which a poem is read and affect the reader’s experience. A well-placed line break can make a situation suspenseful, draw attention to a certain word, or give an impression of surprise. Stanzas, groups of lines separated by spaces, are used to break up the poem into distinct sections, creating logical divisions in the flow of ideas or emotions. Stanzas also allow the poet to introduce different moods or shifts in tone.
Crafting Powerful Imagery
The Importance of Imagery
Imagery is a tool in poetry that helps in painting vivid pictures in the reader’s mind. It makes the how to write a poem come alive by appealing to the senses, thus giving the readers a feeling that they are practically experiencing the scene or emotion. Strong imagery can deepen the meaning of the poem, making abstract ideas more concrete and tangible. For instance, a description like “a sky painted in shades of pink and gold” evokes a beautiful and tranquil atmosphere, enabling the reader to visualize the scene more clearly and emotionally connect with the content.
Using Sensory Details
To create immersive imagery, the poet should call to the five senses of human beings: sight, sound, taste, touch, and smell. These sensory details transport the reader into the world of the how to write a poem with a more emotional or visceral response. For instance, a poet can evoke a sharp tang in the zest of lemon (taste), the rustling leaves from a gentle breeze blowing by (sound), or even the roughness in a crumbling wall (touch). Using sensory details, the poet is in a position to express not only the physical characteristics of a scene but also the emotions and atmosphere that come with it.
Metaphors and Similes
Metaphors and similes are two common devices used to enhance imagery by drawing comparisons. A metaphor states that one thing is another: “The world is a stage.” A simile, on the other hand, uses “like” or “as” to compare two things: “Her laughter was like music.” Both devices create vivid pictures in the mind and help deepen the meaning of a poem by linking two seemingly unrelated things. Metaphors and similes can also convey complex emotions and ideas more effectively than literal language.
The Art of Sound in Poetry
Rhythm is the pattern of beats within a poem. The beats are created by a pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables. Meter denotes a specific, organized rhythm that can be found in a poem. Common meter includes iambic pentameter and trochaic tetrameter. Rhythm can affect the reading of a how to write a poem and interpretation significantly. A regular meter will give a steady and comfortable impression; an irregular meter creates a chaotic or tense mood. Poets choose rhythm and meter carefully to reflect the mood of their poem and guide the reader through its emotional journey.
Rhyme and Alliteration
Rhyme, or the repetition of similar sounds, frequently at line endings, stands out among the more visible devices found in poetry. Indeed, rhyming works musically, aids memorization, and emphasizes words and their meanings. Some examples of ways in which to structure the use of rhymes in verse are the arrangements in pairs. Strategic placement of this sound feature reinforces the auditory movement of the poem through rhythm, meter, or syllable count. Another effective sound device is alliteration, which involves the repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words.
Sound Devices like Assonance and Consonance
Assonance and consonance are rather more subtle sound devices, adding musicality to the poem. Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within words, such as “mellow yellow”; consonance is the repetition of consonant sounds, often at the end of words, like “bitter butter.” Both of these devices contribute to the texture of the how to write a poem, adding depth to its sound and rhythm. When used well, assonance and consonance can enhance the auditory quality of the poem and make it even more engaging for the reader.
Writing with Emotion
Channeling Emotion in Your Writing
To write with emotion, you must first tap into your personal experiences and feelings. Authenticity is key to infusing emotion into your work. Whether you are writing poetry, fiction, or personal essays, starts by reflecting on moments in your life that moved you—whether they were moments of joy, sorrow, love, or anger. Let those feelings well up and then drop naturally onto the page with vibrant language, sensory detail, and metaphor that will say what you have felt.
The Role of Vulnerability
Vulnerability is the heart of emotional writing. When you let go and allow yourself to be honest and open with your emotions, you are making space for others to connect to your story. It doesn’t mean telling absolutely everything that is going on in your life, but it does mean being congruent with your inner self in thought and emotion. On paper, vulnerability can take a raw form and often connect with the audience rather powerfully because they can sense the sincerity in those words. Writing from within your vulnerabilities invites others to engage in your story on a deeper level that feels honest and relatable, which will ultimately make your words more effective.
Connecting with the Reader
Writing with emotional honesty helps to bridge the gap between you and your reader. Emotional writing allows for universal experiences to be shared, thus creating an empathetic connection. Your readers may never have experienced the same circumstances that you have, but through your writing, they can experience your emotions. Whether it is the thrill of new love, the ache of loss, or the bitter anger of words unexpressed, your feelings become an expressway to shared humanity.
Revising and Editing Your Poem
The Revision Process For many poets, the first draft of any poem is an unfinished and rough thing. Still, it provides that beginning. Now, the revision process is where the magic happens-this is where you refine, reshape, and clarify your ideas. Revising gives you the chance to strengthen your poem’s emotional impact, flow, and clarity. When you revise, take a moment to step away from your work and look at it with fresh eyes. This will enable you to notice places where you may want to make improvements, whether in word choice, structure, or pacing.
Tips for Editing
Once you have revised your how to write a poem, it is now time to edit. A very good way to do this is by reading your poem aloud. You may notice the way certain lines sound and the overall flow. You want to cut unnecessary words; every word in your poem should work. Do not be afraid to cut sentences that do not contribute to the meaning or effect of your how to write a poem. Work at clarifying by simplifying sentences and removing repetition of ideas.
Seeking Feedback
Once you have made your revisions, it’s now time to get feedback. Share your poem with peers you trust, writing groups, or mentors who give you constructive critique. You’ll be surprised at what an outside perspective can catch that might not be clear to your readers. Don’t take any criticism personally; this is actually a chance to make your work stronger. This can give you valuable insights into details that you may have overlooked, thereby enabling you to adjust your how to write a poem to a much better emotional appeal. Writing is all about maturing and improving, a process that happens bit by bit.
How Arvin AI Can Enhance Your Poem Writing
Uniquely powerful as a set of tools powered by AI which enhance the quality of your poem by polishing your concepts, your vocabulary, your poems’ shapes their rhythm and rhyme. In this article, we are to explain how Arvin AI will prove its potential to turn the game around for you in the art of poetic composition.
Key Features of Arvin AI
AI-Driven Suggestions on How to Improve Your Writing
Arvin AI provides intelligent suggestions to elevate your how to write a poem. Based on your writing style and content, it provides real-time suggestions on how to select words, write sentences, and be more descriptive. This allows us to transform your thoughts into more forceful, striking sentences.
Language Enhancement Tools
Arvin AI’s language enhancement tools will help you make your poetry more vivid and precise, providing you with synonyms, descriptive words, and expressions that will get the message of your emotions across. With these tools, you can take basic writing to extraordinary, adding depth and emotion to every line.
Poem Structure and Style Assistance
Whether you are writing free verse or following a traditional form, such as a sonnet or haiku, Arvin AI can help you structure your poem. It suggests ways in which you can break up your ideas into stanzas, lines, and verses that flow cohesively, making it easier to express your thoughts in a structured manner.
Rhyming and Rhythm Guidance
For poets working with rhyme or meter, Arvin AI offers suggestions for rhyming and rhythm. Be it a perfect rhyme scheme or the improvement of the flow of your lines, Arvin AI helps in keeping your poem at the right cadence and musicality.
Steps to Use Arvin AI for Poem Writing
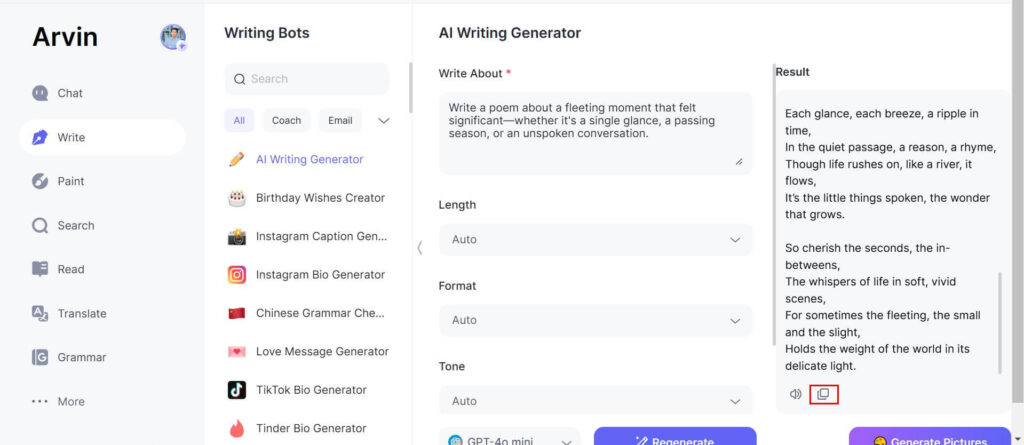
Step 1: Sign Up: To get started with Arvin AI, log in to their website and create an account. By doing this, you will gain access to all the great tools which will enhance your writing experience.
Step 2: Create Project: After having logged in, it is time to start a new project by selecting the style of poetry one wants to write, whether free verse, specific form, or rhyme scheme.
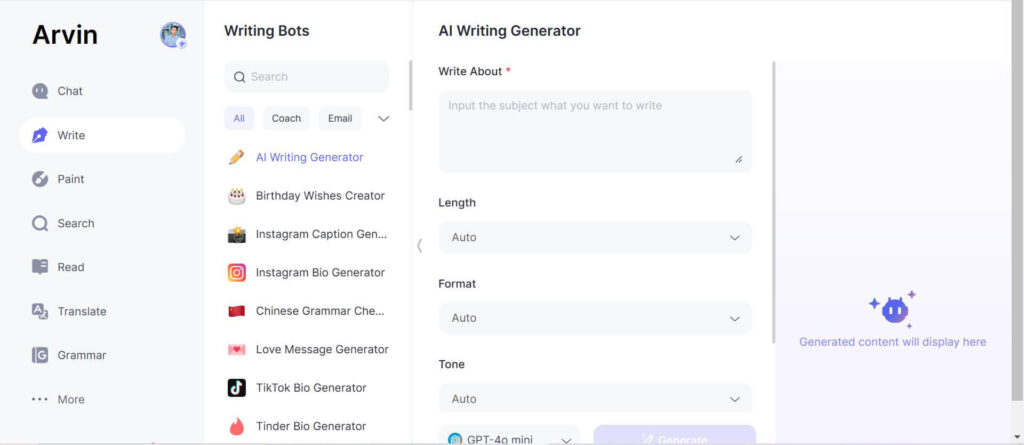
Step 3: Provide Initial Lines: Next, include your initial ideas, whatever lines, themes, or word you want to work off of. Arvin AI will take your input and start making suggestions based on the style you have chosen.
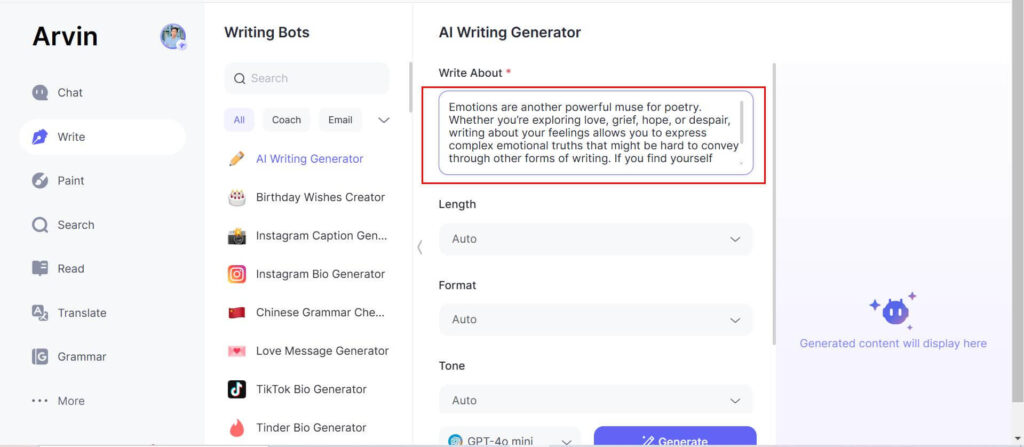
Step 4: Let Arvin AI Suggest Improvements: Arvin AI will give you suggestions to make your writing better, including vocabulary improvement, line breaks, and rhyming/rhythm options.
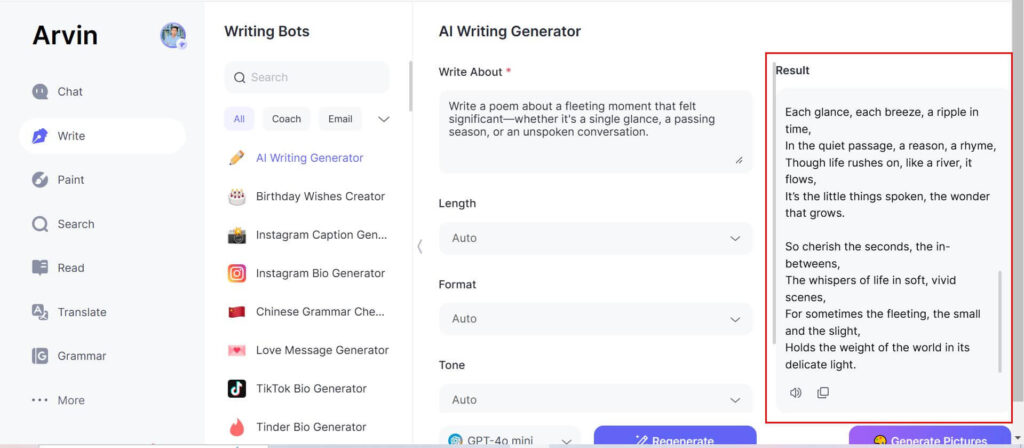
Step 5: Edit and Finalize: Go through your poem, refine the edits after receiving suggestions from Arvin AI, and put the final touches on your work. You can either take the AI’s suggestions as inspiration or make your own adjustments to make the how to write a poem truly your own.
Conclusion
Poetry is a craft that improves through repetition, and Arvin AI can take your poetic work to the next level of how to write a poem. With language augmentation, rhythm, and rhyme suggestions, it will be simple to transform your thoughts into rousing poems. Enjoy the path, experiment with the Arvin AI, and compose poems that bewitch and touch your readers. Try Arvin AI, next poets’ tool, and your verse will fly.
FAQs
1. How does Arvin AI help me improve my poem writing?
Arvin AI provides smart suggestions to improve language, structure and style in the writing of the poem. It provides suggestions about word choices, deals with rhyme schemes and rhythm, and provides information on how to write a poem. They are free verse poems and regular poems.
2. Is Arvin AI suitable for both beginners and experienced poets?
Yes, it is designed for assisting the poet of every caliber, from the complete novice needing guidance in structuring lines and choosing the right words to expert poets looking for ways to finalize their style, rhythm, and rhyme scheme.
3. Must I be a pro poet to efficiently work with Arvin AI?
No, Arvin AI is easy to use and available for all poets, whether beginners or experienced writers; it gives great suggestions for improving your work without requiring professional experience.
4. How important is regular practice in writing poetry?
Practice is key to better poetry writing. You learn about rhythm, structure, and language more and more as you write. Arvin AI can help you a great deal, but to become a better poet, the most important thing you must do is practice regularly.
5. Can I publish my poem after using Arvin AI’s suggestions?
Yes, you can refine your poem with the help of Arvin AI and then finalize it for publishing. While the AI gives suggestions for improvement, you are at liberty to maintain full creative control over your poem before sharing it with others.






